Int’l Tourism Crash May Cost Global Economy $4 Trillion, Says Report
The crash in international tourism due to the coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic could cause a loss of more than $4 trillion to the global GDP for the years 2020 and 2021, according to an UNCTAD (United Nations Conference on Trade and Development) report released on Wednesday.
According to the UNCTAD, the estimated loss has been caused by the pandemic’s direct impact on tourism and its ripple effect on other sectors closely linked to it.
The report, jointly presented with the UN World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), says international tourism and its closely linked sectors suffered an estimated loss of $2.4 trillion in 2020 due to direct and indirect impacts of a steep drop in international tourist arrivals.
A similar loss may occur this year, the report warns, noting that the tourism sector’s recovery will largely depend on the uptake of Covid-19 vaccines globally.
According to the report, the asymmetric roll-out of vaccines magnifies the economic blow tourism has suffered in developing countries, as they could account for up to 60 percent of the global GDP losses.
The tourism sector is expected to recover faster in countries with high vaccination rates, such as France, Germany, Switzerland, the United Kingdom and the United States, the report says.
But experts don’t expect a return to pre-COVID-19 international tourist arrival levels until 2023 or later, according to UNWTO.
The main barriers are travel restrictions, slow containment of the virus, low traveller confidence and a poor economic environment.
Up to $1.8 trillion loss expected in 2021
A rebound in international tourism is expected in the second half of this year, but the UNCTAD report still shows a loss of between $1.7 trillion and $2.4 trillion in 2021, compared with 2019 levels.
The report assesses the economic effects of three possible scenarios – all reflecting reductions in international arrivals – in the tourism sector in 2021.
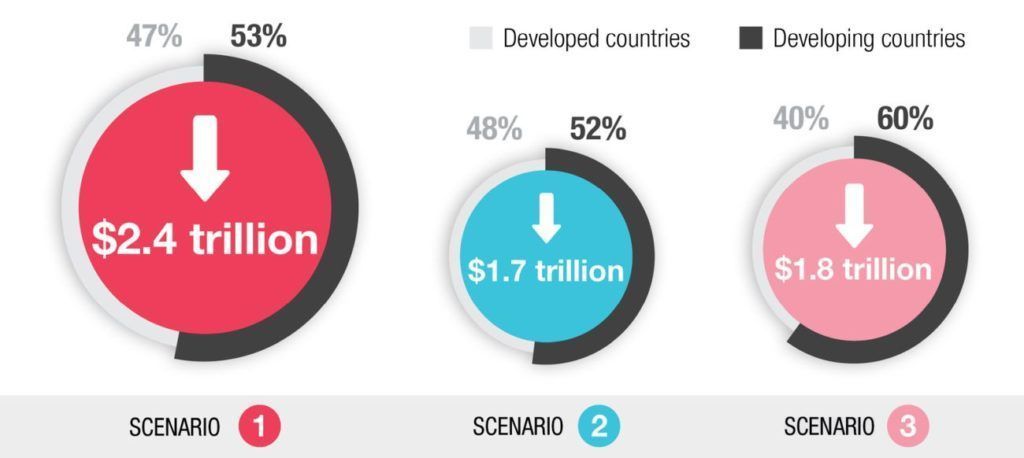
As tourism falls world GDP takes a hit in 2021 (3 alternative scenarios). Source: UNCTAD based on GTAP simulations
The first scenario, projected by UNWTO, reflects a reduction of 75% in international tourist arrivals – the most pessimistic forecast – based on the tourist reductions observed in 2020.
In this scenario, a drop in global tourist receipts of $948 billion causes a loss in real GDP of $2.4 trillion, a two-and-a-half-fold increase.
The second scenario reflects a 63% reduction in international tourist arrivals, a less pessimistic forecast by UNWTO.
And the third scenario, formulated by UNCTAD, considers varying rates of domestic and regional tourism in 2021.
It assumes a 75% reduction of tourism in countries with low vaccination rates, and a 37% reduction in countries with relatively high vaccination rates, mostly developed countries and some smaller economies.
Losses worse than previously expected
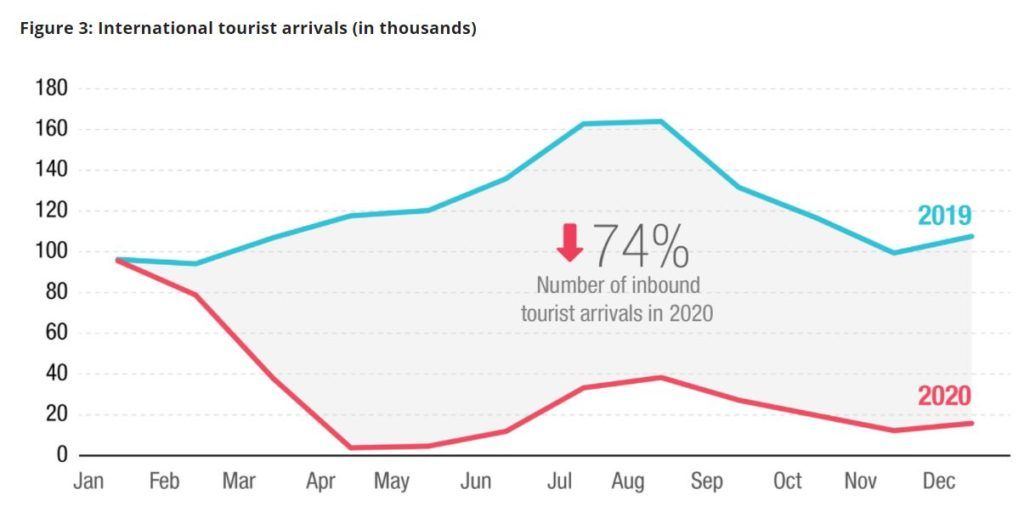
According to UNWTO, international tourist arrivals declined by about 1 billion or 73 percent between January and December 2020. In the first quarter of 2021, the UNWTO World Tourism Barometer points to a decline of 88 percent.
Developing countries have borne the biggest brunt of the pandemic’s impact on tourism. They suffered the largest reductions in tourist arrivals in 2020, estimated at between 60 percent and 80 percent.
The most-affected regions are North-East Asia, South-East Asia, Oceania, North Africa and South Asia, while the least-affected ones are North America, Western Europe and the Caribbean.
Press here for the UNCTAD’s full analysis.